Trying to choose between a recumbent bike vs upright bike for your workouts? This article breaks down the key differences—comfort, muscle engagement, joint impact, and workout intensity—to help you decide which bike aligns with your fitness goals. Keep reading to find your ideal match.
Key Takeaways
-
Recumbent bikes provide ergonomic support, reducing strain on the back and joints, making them ideal for users with mobility limitations or back issues.
-
Upright bikes engage a wider range of muscles and offer higher calorie burn potential, making them suitable for individuals seeking intense workouts and weight loss.
-
Choosing between recumbent and upright bikes should be based on personal fitness goals, available space, and comfort preferences.
Design and Comfort Differences
If you prioritize comfort and back support, recumbent bikes are generally better than upright bikes.

When it comes to design and comfort, most recumbent bikes offer ergonomic support, which enables users to maintain comfort over longer periods. These bikes feature a reclined seating position with legs extended in front, promoting a relaxed seating position that reduces strain on the back and joints. Recumbent bikes tend to have a chair-like seat that supports the lower back, providing added comfort during workouts. Understanding how recumbent bikes work can enhance the overall experience.
In contrast, upright bikes mimic traditional bicycle seating, requiring users to sit upright with pedals located directly under the hips in an upright position. This positioning can place additional strain on the body, particularly on the lower back and joints. The bike seat on upright bikes is typically smaller, which might lead to discomfort during extended workout sessions.
Overall, the seated position of recumbent bikes offers more comfort and support, particularly for individuals with back issues or those who prefer an adjustable seat in a relaxed workout setting. These design differences are key in deciding which bike suits your needs best in the upright vs recumbent comparison.
Muscle Engagement and Workout Intensity
Both recumbent and upright bikes work the glutes, thighs, hamstrings, and calves, but upright bikes also engage the core, arms, shoulders, and back for a more full-body workout.

Upright bikes are designed to replicate traditional cycling, offering a vigorous workout that engages a wider range of muscles.
Upright bikes engage a wider range of muscles, including:
- Biceps and triceps (through upright posture and handlebar support)
- Shoulders and arms (from maintaining balance and grip)
- Core and abs (due to the need for trunk stabilization)
- Glutes, thighs, and calves (similar to recumbent bikes but with greater intensity)
In contrast, recumbent bikes primarily target:
- Quadriceps and hamstrings (via forward pedaling motion)
- Glutes and calves (with less intensity than upright bikes)
- Minimal upper body and core engagement due to the supported, reclined position
Research has found that upright bikes make your core and back muscles work harder than recumbent bikes, leading to better full-body engagement. (Bouillon et al., 2016 [1]).
This makes upright bikes ideal for people seeking a more comprehensive workout. The ability to engage different muscle groups ensures a challenging workout that can enhance overall fitness levels with the right fitness equipment.
On the other hand, recumbent bikes primarily target the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves, making them better suited for low-to-moderate intensity workouts. While they may not provide the same level of upper body engagement as upright bikes, they still offer excellent cardiovascular workouts and can be an effective part of a fitness journey.
If you seek a more intense workout that engages various muscle groups, upright bikes are ideal. Conversely, for a low-impact cardio workout focused on lower body muscles, recumbent bikes are a great option.
Impact on Joints and Accessibility
Recumbent bikes are easier on the joints than upright bikes because their reclined design reduces pressure on the knees, hips, and lower back.

This aligns with guidance from the National Institute on Aging [2], which recommends supportive, joint-friendly equipment like recumbent bikes for older adults or those with mobility concerns. The design of these bikes supports joint health by promoting the production of synovial fluid, which helps lubricate the joints. Compared to upright bikes, recumbent bikes provide a gentler workout that is easier on all joints, making them a safer option for individuals with mobility limitations.
The lower center of gravity of recumbent bikes reduces the risk of falls, enhancing their accessibility for beginners and those with fragile joints. This makes them particularly beneficial for older adults and individuals recovering from injuries, as the supportive design allows for safer and more comfortable workouts.
In contrast, upright bikes require users to maintain balance and stability, which can be challenging for individuals with joint issues or discomfort. Unlike upright bikes, traditional upright bikes offer a more traditional cycling experience, but may not be as suitable for those with joint concerns or those seeking a low-impact workout option. A stationary bike can also be a good alternative for those looking for a comfortable workout solution.
Cardiovascular Benefits
Both upright and recumbent bikes improve cardiovascular health, but recumbent bikes do so with less joint stress and greater comfort.
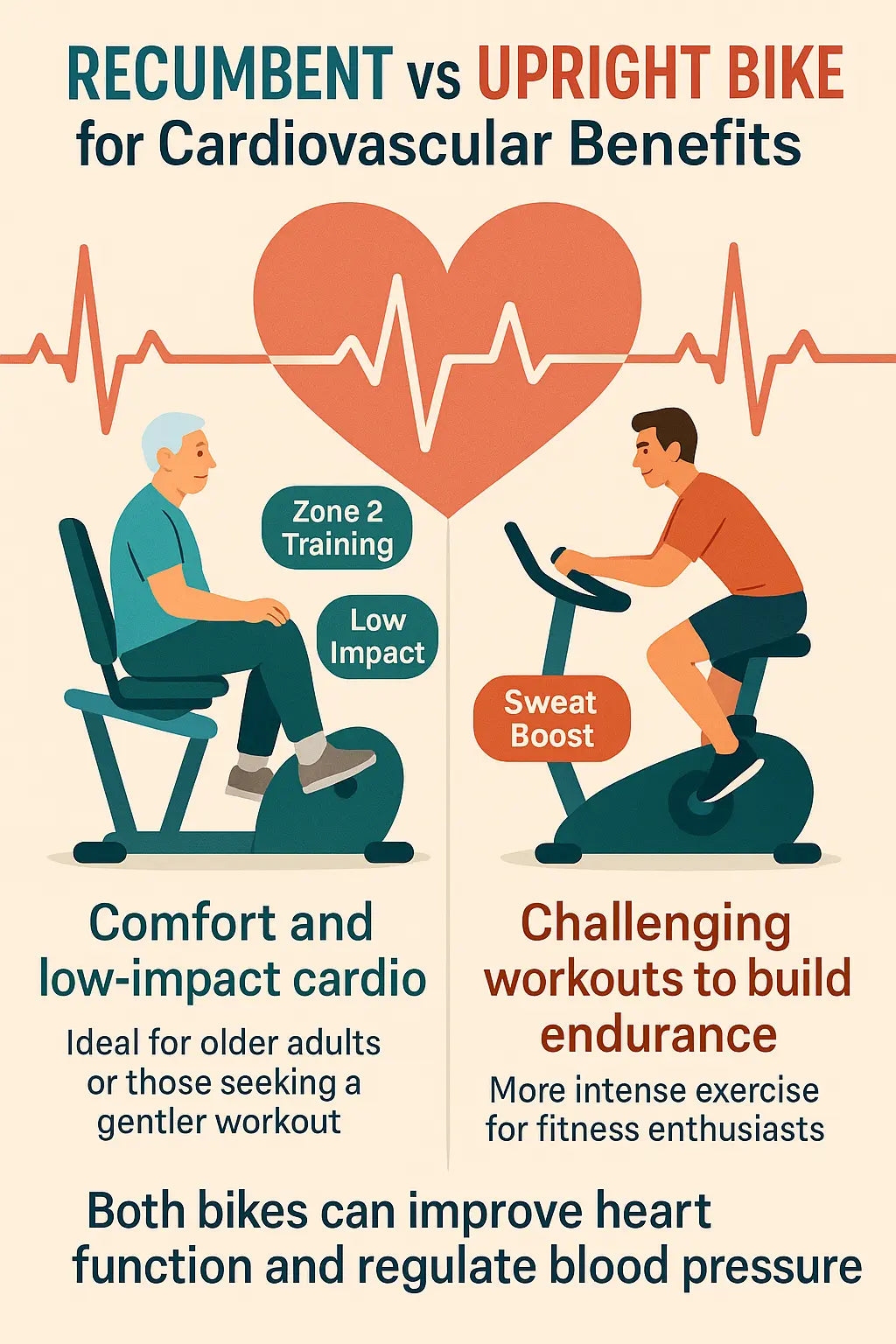
Upright bikes are excellent for building endurance and improving cardiovascular fitness due to their more intense workout capabilities. These upright exercise bikes are designed to provide challenging workouts that can significantly enhance heart function and regulate blood pressure, making them a popular choice for fitness enthusiasts seeking to boost their cardiovascular health with an upright stationary bike through upright cycling.
Both upright and recumbent bikes can enhance cardiovascular health by improving heart function and regulating blood pressure, supported by the American Heart Association's recommendation [3]. Whether you prefer the intense workouts offered by upright bikes or the low impact cardio workout provided by recumbent bikes, both options can contribute to better heart health and overall cardiovascular fitness.
For older adults or those seeking a gentler workout, recumbent bikes provide excellent cardiovascular exercise with added comfort and support. Both exercise bikes and an exercise bike type can help you achieve your cardiovascular fitness goals, regardless of your fitness level. Incorporating cardio equipment into your routine can further enhance your workouts.
Weight Loss and Calorie Burning
Upright bikes burn more calories than recumbent bikes due to higher workout intensity, but recumbent bikes allow for longer, more comfortable workouts that support steady weight loss over time.

When it comes to calorie burning and weight loss, upright bikes have the edge due to:
-
Their higher calorie burn potential.
-
Engagement of a wider range of muscles, allowing for more intense workouts that can burn more calories overall.
-
The ability to perform high-intensity interval training (HIIT), which can lead to a higher calorie burn compared to steady-state workouts. These factors make upright bikes ideal for those seeking significant weight loss.
Source: American Council on Exercise (ACE) – “HIIT vs. Steady-State Training: Which One is Best for Your Clients??” [4]
Recumbent bikes, though typically burning fewer calories than upright bikes, can still aid weight loss when paired with a balanced diet. Their comfort and ease of use promote longer workout sessions, increasing calorie burn over time. Enjoying the bike you use is key to maintaining regular workouts and achieving weight loss.
Overall, both recumbent and upright bikes can be effective tools for weight loss, with the choice depending on personal preferences and fitness goals. The type of workout performed, whether HIIT or steady-state, significantly influences overall calorie expenditure and weight loss outcomes.
Space and Maintenance

Space and Storage Considerations
While recumbent bikes generally have a larger footprint than upright bikes, they still fit comfortably in most home settings. Their extended design may take up more floor space, but many models are designed with home users in mind and don’t require a separate workout room.
Upright bikes, on the other hand, are more compact and easier to tuck into small corners or tighter spaces, making them ideal for apartments or multi-use rooms where space is limited. For households with enough room, a recumbent bike remains a practical choice—especially for those prioritizing comfort and joint support.
Maintenance and Durability
Both recumbent and upright bikes require regular maintenance to ensure they remain in good working condition. Weekly checks should focus on tightening hardware and lubricating moving parts to prevent wear and tear. Monthly maintenance involves lubricating the chain drive and ensuring all hardware is secure. Using antibacterial solutions for cleaning is recommended to maintain the bike’s appearance.
Inspecting and lubricating resistance pads is necessary for bikes with contact resistance systems to ensure smooth operation. Regular maintenance is essential to keep both recumbent and upright bikes durable and functional, providing users with a reliable fitness experience.
Best Recumbent Bikes

Recumbent bikes are praised for their safety, comfort, and cardiovascular benefits, making them especially popular among older adults and individuals in recovery. Among the top choices, the VANSWE RB405 Recumbent Bike offers a premium blend of functionality, comfort, and accessibility.
Product Link: RB405 Recumbent Stationary Bike 90% Pre-assembled
Why the Vanswe RB405 Stands Out
The RB405 features an ultra-quiet magnetic resistance system with 8 adjustable levels, supported by an 11-lb flywheel for smooth operation under 10dB—ideal for shared living spaces. Its step-through design and ergonomic seat with back support make it perfect for seniors, users with limited mobility, or anyone prioritizing joint-friendly workouts.
It includes:
-
A 400 lb weight capacity for stability and inclusivity
-
A digital LED display tracking time, speed, distance, heart rate, and calories burned
-
Bluetooth connectivity compatible with Kinomap and Zwift for interactive training
-
Adjustable seat supporting users with 26"–41" inseam lengths
💡 Therapeutic and Home-Friendly Design
The RB405 is not only a great tool for fat burning and endurance training, but it's also widely used in physical therapy settings. Its low-impact, joint-safe design helps users maintain fitness while minimizing strain on knees, hips, and lower back.
⭐ Customer Favorite
Users highlight its:
-
Ease of assembly
-
Sturdy and compact design
-
Smooth, quiet ride
-
App compatibility for immersive cycling experiences
Whether you're building a home gym or seeking a reliable tool for daily fitness, the VANSWE RB405 Recumbent Bike is a smart investment for long-term health and comfort.
Choosing the Right Bike for Your Fitness Goals
Choosing the right bike depends on your fitness goals and health conditions. Upright bikes may better build endurance and suit fitness enthusiasts and younger people without physical limitations. They offer a challenging workout that can significantly boost cardiovascular fitness.
Conversely, recumbent bikes benefit seniors aiming to enhance core strength and balance. Their comfort and support facilitate longer workout sessions, increasing calorie burn and fitness over time. Both recumbent and upright bikes effectively burn calories, with higher calorie burn potential rising with longer and more intense workouts.
When selecting a bike, consider factors such as your budget, available space, and the intensity of the workouts you plan to perform. Considering these factors will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your fitness goals and ensures a satisfying exercise experience.
Summary
In summary, both recumbent and upright bikes have unique features and benefits that cater to different fitness goals and preferences. Recumbent bikes offer superior comfort and support, making them ideal for individuals with joint concerns or those seeking a low-impact workout. Upright bikes, with their more intense workout capabilities, are better suited for those looking to engage a wider range of muscles and achieve higher calorie burn.
Ultimately, the choice between recumbent and upright bikes depends on your personal fitness goals, health conditions, and preferences. By considering the factors discussed in this guide, you can select the bike that best aligns with your needs and embark on a successful fitness journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which bike is better for weight loss, a recumbent bike or an upright bike?
Upright bikes are better for weight loss as they provide higher calorie burn potential through greater muscle engagement and the ability to perform high-intensity interval training.
Are recumbent bikes suitable for individuals with joint pain?
Recumbent bikes are suitable for individuals with joint pain, as they reduce stress on the knees and hips, making exercise more comfortable. This makes them an ideal choice for those experiencing mobility limitations.
Can both recumbent and upright bikes improve cardiovascular fitness?
Both recumbent and upright bikes can effectively enhance cardiovascular fitness by improving heart function and regulating blood pressure. Each type offers a valuable option for achieving your fitness goals.
How do recumbent bikes accommodate different user heights?
Recumbent bikes accommodate different user heights through adjustable seats, ensuring a comfortable fit for a wide range of individuals. This feature allows for a customized riding experience, enhancing comfort and support while cycling.
What maintenance is required for exercise bikes?
Regular maintenance of exercise bikes requires weekly checks to tighten hardware and lubricate moving parts, along with monthly chain drive lubrication and routine cleaning with antibacterial solutions. By following this schedule, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity of your bike.
Related Article
Upright vs Recumbent
Upright Bike vs Recumbent Bike: Which One Will You Actually Stick to for 30 Days?
Recumbent Bike vs Upright Bike Muscle Groups: What's the Difference?
The Upright Recumbent Bike: Features and Benefits Explained
Stationary vs Recumbent Bike: Which One Is Right for You?
The Difference Between Recumbent Bike and Upright Bike?
Recumbent Bike vs Upright Bike for Weight Loss
Other Comparison
Recumbent Bike vs Upright Bike
Recumbent Bike vs Recumbent Stepper
Recumbent Bike vs Rowing Machine
Reference
- Bouillon, L., Baker, R., Gibson, C., Kearney, A., & Busemeyer, T. (2016). COMPARISON OF TRUNK AND LOWER EXTREMITY MUSCLE ACTIVITY AMONG FOUR STATIONARY EQUIPMENT DEVICES: UPRIGHT BIKE, RECUMBENT BIKE, TREADMILL, AND ELLIPTIGO®. International journal of sports physical therapy, 11(2), 190–200.
- National Institute on Aging. (n.d.). Three types of exercise can improve your health and physical ability. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/exercise-and-physical-activity/three-types-exercise-can-improve-your-health-and-physical
- American Heart Association. (n.d.). American Heart Association recommendations for physical activity in adults and kids. https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/fitness/fitness-basics/aha-recs-for-physical-activity-in-adults
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Weight loss: Choosing a diet that's right for you. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/weight-loss/art-20048466
Table of Contents
Latest Articles







